Introduction to Beego’s MVC
Beego uses a typical Model-View-Controller (MVC) framework. This diagram illustrates how request handling logic is processed:
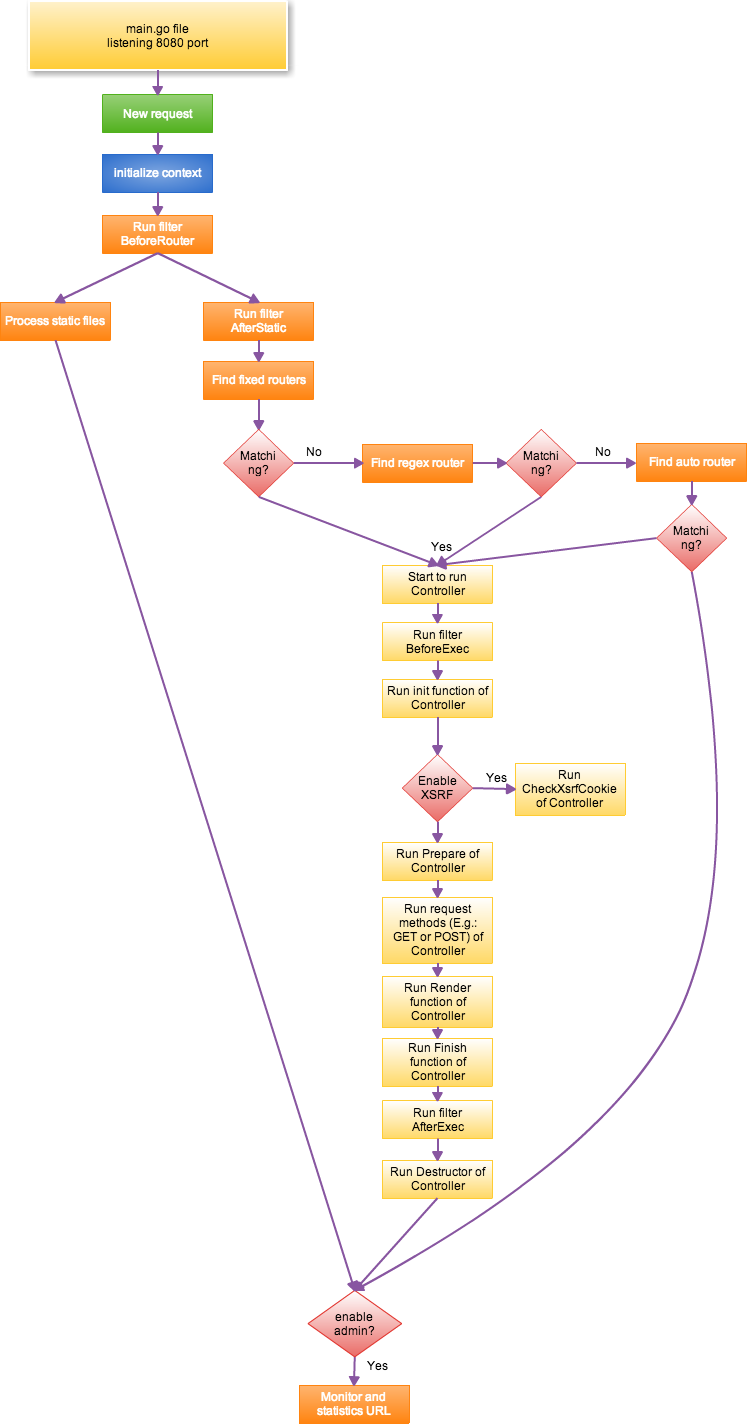
The whole logic handling process is explained below:
- Data is recieved from the listening port. The listening port is set to 8080 by default.
- Beego begins processing the requested data after the request reachs port 8080
- The Context object is initialized. WebSocket requests will be set as Input after the request method has been verified as a standard method (get, post, put, delete, patch, options, head) in order to protect from hostile attack.
- If the
BeforeRouterfilter has been set by the user it is executed. IfresponseWriterhas output data while executing this filter the request will be finished and the supervise checking step (see item 21) will be performed next. - Start handling of static files. If the requested url matches the prefix set by
StaticDir, theServeFilein thehttppackage will be used to handle the static file requests. - If the request is not for a static file, and the session module is enabled, the session module will initialize. An error will occur if session is being used in the
BeforeRouterfilter (see item 4). Use theAfterStaticfilter (see item 7) instead to avoid this error. - The
AfterStaticfilter is executed. IfresponseWriteralready has output data while executing this filter the request will be finished and the supervise checking step (see item 21) will be performed next. - After all filters have been executed Beego will start to match any requested urls with fixed routing rules. These connections will only be made if the whole string matches. For example:
/hellodoes not match the url of/hello/world. If any matching pairs are found the appropriate logic will execute. - Regex matching is executed based on the order that the user added. This means the order of the regex routing rules will affect Regex matching. If any matches are found the appropriate logic will execute.
- If the user registered
AutoRouter,controller/methodwill be used to match the Controller and method. If any matches are found the appropriate logic will execute. Otherwise the supervise checking step (see item 21) will be performed next. - If a Controller is found Beego will start this logic.
BeforeExecwill execute first. IfresponseWriteralready has output data while executing this filter the request will be finished and the supervise checking step (see item 21) will be performed next. - Controller will start executing the
Initfunction to initialize basic information.bee.Controllerwill usually be initialized as part of this item, so modifiying this function is not recommened while inheriting the Controller. - If XSRF is enabled it will call
XsrfTokenofController. If this is a POST requestCheckXsrfCookiewill be called. - The
Preparefunction ofControllerwill be executed. This function is normally used by the user to launch initialization. IfresponseWriteralready has data while executing this filter it will go directly to theFinishfunction (see item 17). - If there is no output the user registered function will be executed. If there is no function registered by the user the method in
http.Method(GET/POST and so on) will be called. This will execute logic inluding reading data, assigning data, rendering templates, or outputing JSON or XML. - If there is no output by
responseWritetheRenderfunction will be called to output template. - Execute the
Finishfunction ofController. This function works as an override to allow the user to release resources, such as data initialized inInit. - Execute the
AfterExecfilter. If there is output it will jump to the supervise checking step (see item 21). - Execute
DestructorinControllerto release data allocated inInit. - If there is no router has been found the 404 page will be shown.
- Eventually, all logic paths lead to supervise checking. If the supervisor module is enabled (default on port 8088), the request will be sent to supervisor module to log data such as QPS of the request, visiting time, and request url.
The next sections will detail the first step of Beego’s MVC, routing: